Credit card
A credit card is issued by a financial institution that allows you to borrow money to make a purchase. According to a recent Experian report, the average American owns 4 credit cards. Credit cards are not only a convenient way for people to buy things with borrowed funds, but they are also great for earning rewards.
What you need to know about paying with credit cards
While a credit card allows a cardholder to buy things instantly online, over the phone or in a store, there are consequences for not paying money back.
Cardholder must repay credit union
You, the borrower, must pay back everything purchased on a credit card. It is not free money.
A credit card balance is the amount the cardholder owes for unpaid purchases. If you carry a balance (i.e., you don't pay off the full credit card balance every month), interest charges apply.
There are two ways to pay off your credit card debt
If you don't pay off a credit card every month, it can have disastrous effects on your financial health. You should choose one of the following options:
- Pay your balance in full and on time (by the bill due date).
- Carry a balance by paying less than the full balance or the minimum payment due.
Credit card payment example
Suppose you apply for a credit card online or through your bank. After one month, you'll have your new credit card with 1.000 US dollars charged. The bank sends you a bill for all purchases you made within the most recent "billing period" (usually a 25 to 30 day period).
Scenario 1: Pay in full and on time
To pay your balance in full and on time, you would give the bank the entire 1.Pay back $000 that you spent in the last billing cycle. If you pay in full (and on time), you won't have to pay any interest or late fees, provided you don't owe any previous debt on that credit card.
Many credit cards offer perks like cash back rewards or travel points. Paying off in full each month is the best way to earn annual rewards over time and still stay debt-free.
Scenario 2: Make the minimum payment
The second option is to carry a balance on your credit card and pay it back over time. For most people, this usually means paying the minimum payment due, although it could also mean paying slightly less than the full balance due.
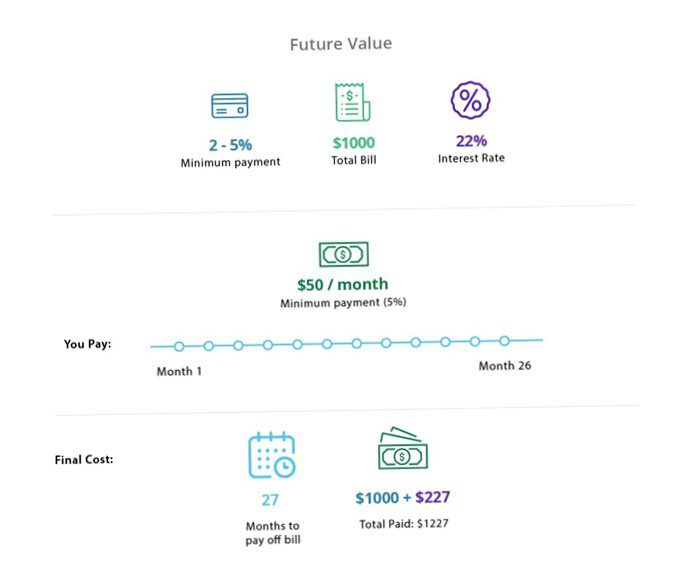
If you pay a fraction of the total amount for the billing cycle, fees will apply. Unless you have a special 0% APR introductory offer, interest will be charged on the remaining balance. Assuming you only pay the minimum (usually between 2% and 5%) of the total bill of 1.000 USD. In this case, you have paid $50 (5%) and the interest rate is 22%. If you continue to pay $50 each month until the balance is paid, you will pay an additional $227.00 in interest. This means that you will have 1.000 US dollars spent and 1.Have repaid $227. At this rate, it would take about 26 months to pay off the card in full.
To avoid interest charges and credit card debt, it is often advisable to pay off your credit card balance in full each month (if possible). Pay off at least your credit card balance before the 0% APR offer disappears.
Credit card terminology you should know
Paying off a credit card balance is only one responsibility of a borrower: it's also the borrower's responsibility to know certain credit card terms and conditions.
What is a credit limit?
Credit cards grant you a certain amount of money that you can borrow during a certain period of time. This is called a credit limit. Credit limit is set by the card issuer based on the cardholder's creditworthiness and credit history.
What determines the credit card interest rate (d. h. APR)?
Interest rate on credit cards typically ranges from 10% to 25%, but can be even higher. A person's credit score and credit history affect the interest rate or APR on the credit card. In general, the higher your credit score, the lower APR you may qualify for.
The interest rates are not set in stone. Lenders may increase the APR if a borrower's credit score deteriorates or if national interest rates increase. Many card issuers offer introductory 0% APR offers for a period of time to incentivize credit card use. These will return a much higher interest rate later on.
What fees and charges do credit cards have?
In addition to interest fees for carrying a balance, many credit cards also have the following fees:
- An annual fee
- Late payment fees
- Fees for exceeding the credit limit
- Advance fees and
- Foreign currency conversion fees
Related: 6 steps to avoid credit card fees
To avoid unpleasant surprises, it is important for the cardholder to read and understand the issuer's disclosure statement.
Credit score basics
Credit scores range from 300 to 850. The higher a person's score, the more creditworthy they are. According to Experian, a good credit score is 700 or higher. An excellent credit score would consider anything over 800. Borrowers with this type of credit score are more likely to qualify for the best credit card offers.
To calculate your credit score, the following information is considered:
- Payment history (35% of score)
- Total amount owed by one person (30% of the score)
- The length of your credit history (15% of your score)
- New lines of credit (10% of score)
- The types of credit accounts such as car loan, mortgage, credit cards (10% of the score)
The credit bureau collects and provides this information to potential lenders and creditors.
How credit cards affect your credit score
Credit cards can help you increase or decrease your credit score depending on how you use them:
Opening and closing accounts
Opening a new account and keeping it in good standing can help boost your credit score. That's because payment history and new lines of credit are calculated into your credit score.
Each time you apply for a credit card, the issuer performs a credit check. This may cause your score to drop a few points, but this is a necessary hit to open a new account. A large number of credit card applications within a short period of time can cause your score to drop even further. It is best to limit the number of uses to avoid this. Closing an account means your credit utilization changes, which in turn can cause your credit score to go down. Instead of closing an account, you can try cutting up the credit card or restricting its use (but keeping the credit line open).
Carry a high balance
The less you use your credit, the more you can increase / maintain your credit score. Remember: the amount of debt you carry can cause credit scores to rise or fall. Paying off your balance each month means you don't have to worry about high balances (and your credit score).
Make late payments
Your payment history is an important part of your credit score calculation. Maintain on-time payments, as late payments will be reflected in your credit report and credit score.
Types of credit cards
There are different types of cards to suit specific needs. The three most common types of credit cards are:
Secured credit cards
A secured credit card can be a good credit-building option for those with zero credit history or bad credit. They are also the easiest credit card to be approved for.
Under this secured card agreement, the cardholder agrees to deposit a certain amount on the card before using it. The amount deposited is the cardholder's credit limit. This reduces the risk to the card-issuing bank, as it can make an advance payment if the cardholder is unable to make a repayment.
Cash Back Credit Cards
With a cash back credit card, you can literally earn 'cash back' on your purchases on a monthly or annual basis. Cash back rewards cards can offer between 1% and 5% back on purchases (meaning cardholders can earn between $1 and $5 per $100).
Travel credit cards
With a Travel Rewards credit card, you can earn points on your purchases monthly or annually. These points can be redeemed for things like airline tickets, hotel stays and travel expenses.
Choosing the best credit card
With so many options, it can be difficult to choose the right credit card for you. However, there are a few tips for choosing one:
- When you build your credit, choose a secured credit card.
- If you want to carry a balance, choose a 0% APR card with a fixed APR after the introductory offer.
- If you're doing a balance transfer, choose a 0% APR card.
- If you can pay off the card each month, focus on the rewards you can receive.
For more tips on choosing the best credit card, check out our article that breaks down credit card offers.
Related: top 5 rewards credit cards of 2019
How to get a credit card
You must be at least 18 years old to obtain a credit card. Below are the basic steps for a credit card:
- Look at your credit score to see where you stand
- Choose a card that offers the most beneficial rewards for your lifestyle.
- Find an introductory offer online that offers either 0% APR or a great sign-up bonus.Read all credit terms to understand fees, interest rates and benefits.
- Fill out an application. You must provide proof of income.
- Wait for approval. Don't apply for any more credit cards until you hear back.
- Once approved, set up an online account with reminders so you don't miss a payment.
How Credit Card Consolidation Works
If you are in major credit card debt, you might consider a credit card consolidation loan. In this case, the lender pays off your credit card debt and issues a new loan with a fixed monthly payment and interest rate. Ideally, this interest rate is lower than your credit card interest rate and your monthly payments are more affordable. A credit card consolidation loan is a valid option for those with overwhelming debt, but you may want to consider a balance transfer first.
What is a balance transfer?
A balance transfer is ideal for borrowers who carry a balance on one or more credit cards (but may be trying to get out of debt). The cardholder can transfer and consolidate existing credit card balances to a balance transfer card. You can pay off this debt at 0% interest for a set period of time.
Related: the top 4 balance transfer credit cards for 2020
A credit card can be a great tool – if used correctly
Using a credit card can either help or hinder your financial position. While you can use a credit card to fund an emergency or pay for a large purchase over time, it's important to have a plan to pay it back – and avoid major credit card debt.